The role of nutrition on inflammation
Inflammation can be caused by viruses, autoimmune disease like rheumatoid arthritis, poor sleep, smoking, obesity and environmental factors such as pollution. Ageing can also be linked to inflammation.
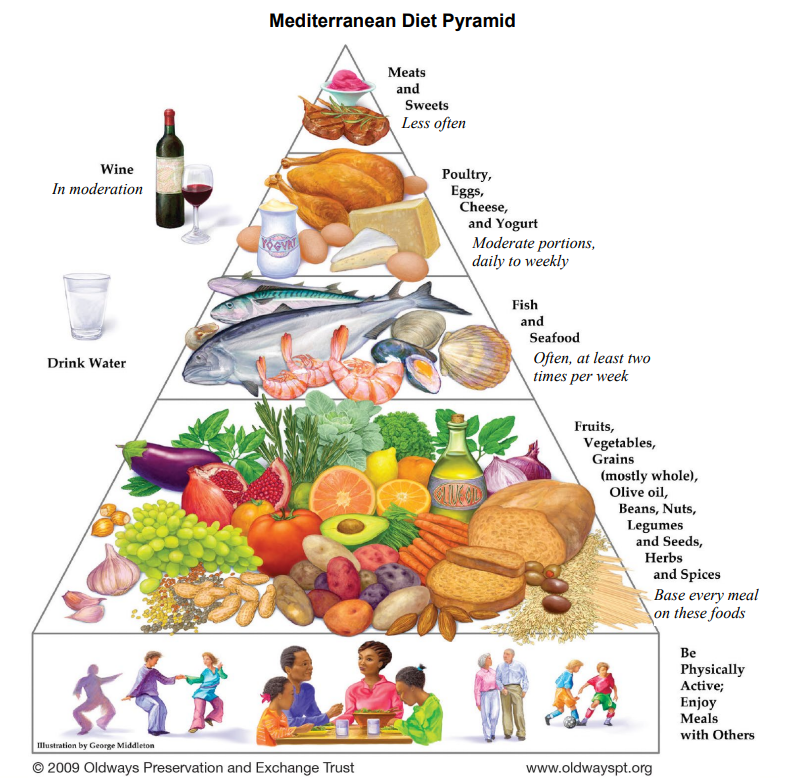
Certain eating patterns have been linked to less of an inflammatory response in the body and this should be where our focus lies rather than vilifying or promoting specific pro and anti-inflammatory foods. The Mediterranean Diet has been one such eating pattern identified to combat inflammation and chronic disease (1). A Mediterranean-style diet is based on these foods:
• vegetables
• fruits
• extra virgin olive oil
• wholegrain breads and cereals
• legumes or beans (e.g. chickpeas, kidney beans or lentils)
• nuts and seeds
• fish and seafood
• onion, garlic and other herbs and spices (e.g. oregano, coriander, cumin etc.
Red meats and sweets are only eaten in small amounts, and processed meats (deli meats, bacon, ham, corned meats, salami or sausages) and packaged foods should be limited to rare occasions. For those who choose to drink alcohol, wine (especially red wine) which is considered a traditional part of the Mediterranean-style diet, should only be consumed in small amounts and with meals.
This style of eating pattern does not just focus on what foods you should eat, but how you eat them. For example, sharing meals with friends and family; eating without distractions (e.g. not in front of the TV); eating slowly so that the taste and flavour of the food can be appreciated; and a focus on preparing fresh foods.
For further support incorporating a Mediterranean-style diet eating pattern into your lifestyle please reach out to book a consultation and I am happy to support with this.
References
Tsigalou C., Konstantinidis, T., Paraschaki A., Stavropoulou E., Voidarou C., Bezirtzoglou E. Mediterranean Diet as a Tool to Combat Inflammation and Chronic Diseases. An overview. Biomedicines. 2020 Jul 8;8(7): 201.